K-Food RAG: AI-Powered Culinary Discovery
Next.jsNestJSPostgreSQLQdrantGoogle GenAIRedis
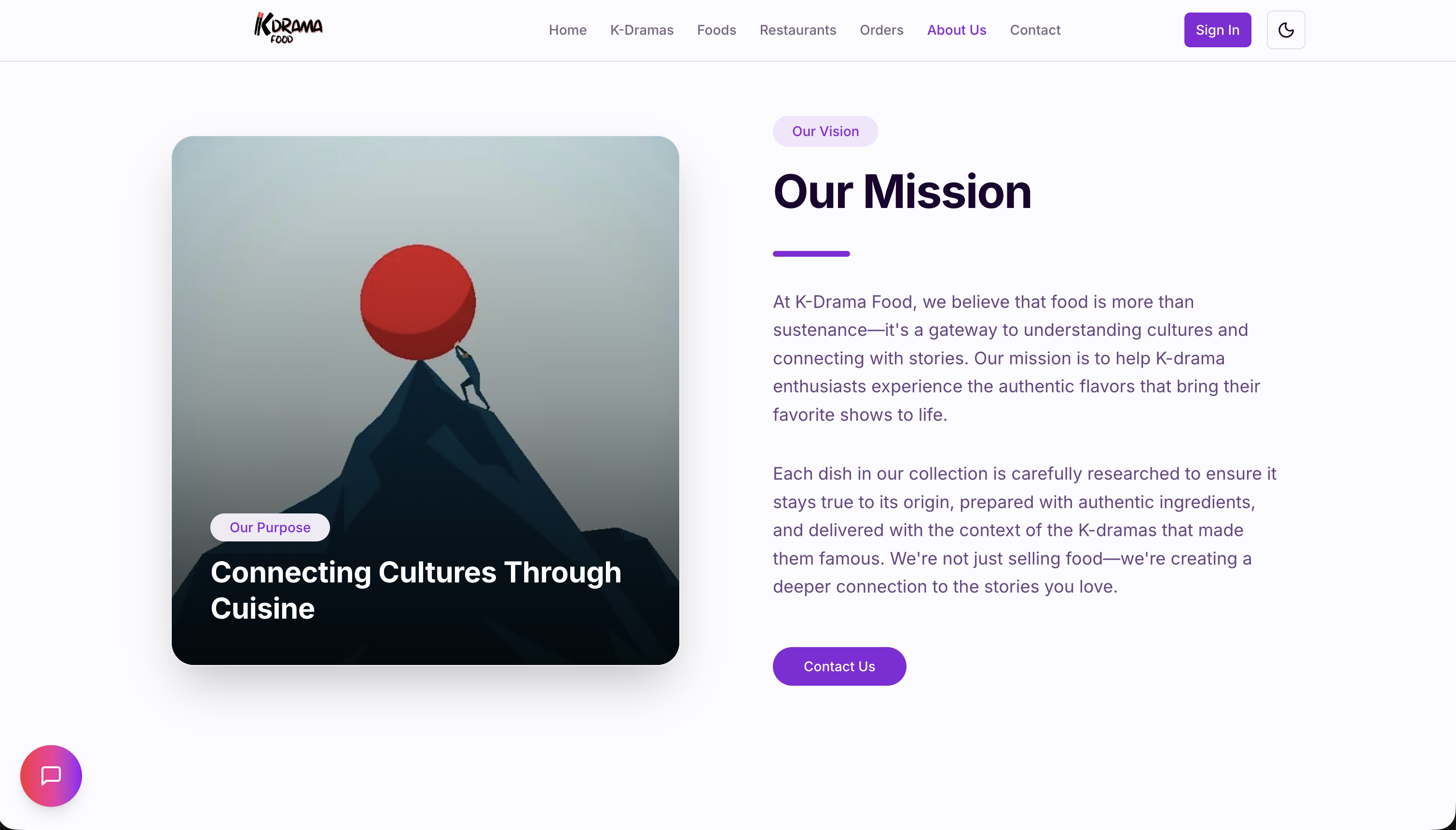
Overview
K-Food RAG is a production-ready system designed to revolutionize how users discover and explore Korean cuisine. By integrating Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with a robust microservices architecture, it provides intelligent, context-aware search results that go beyond simple keyword matching.
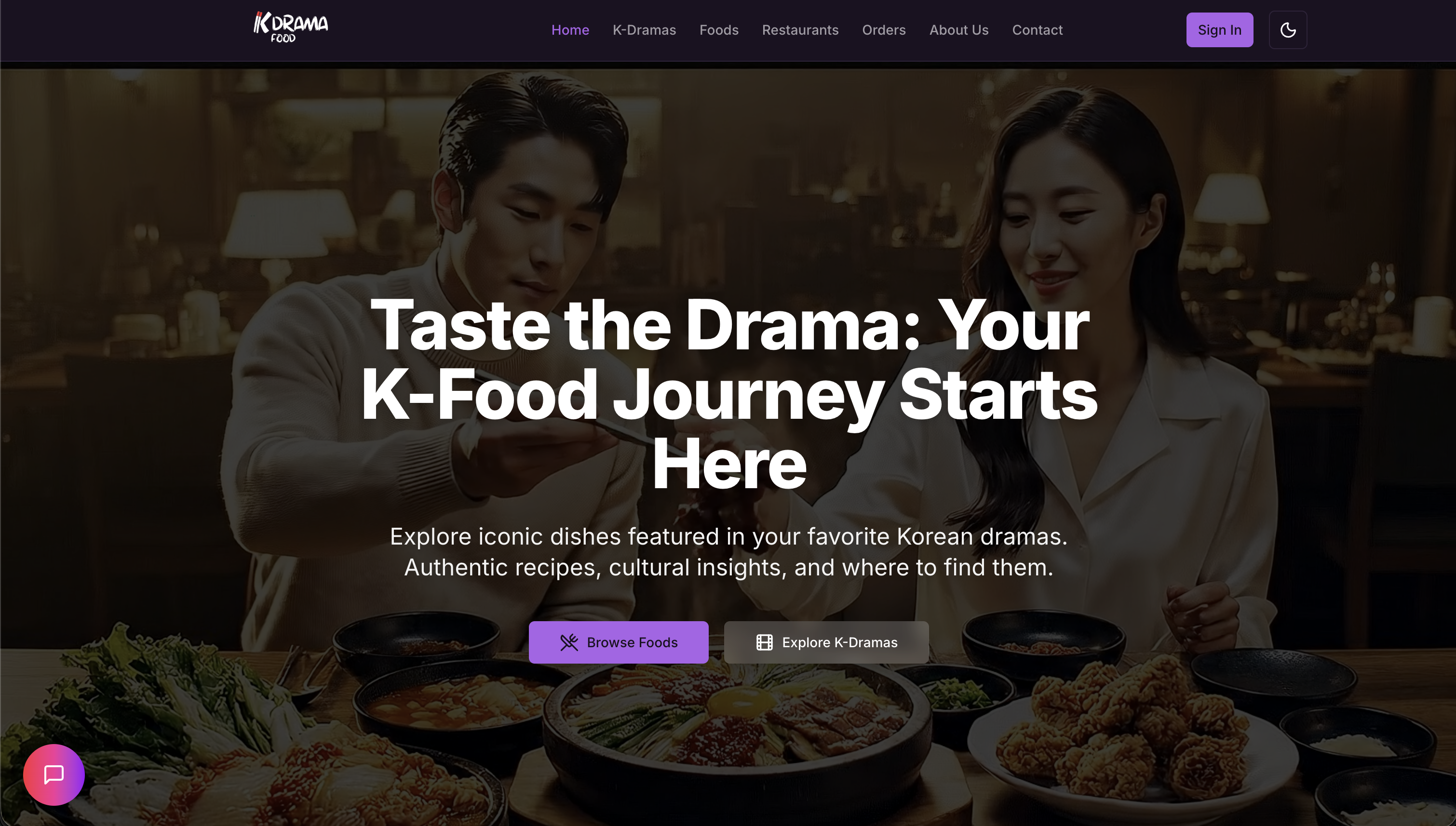
Key Features
🧠 Intelligent Search
- Semantic Understanding: Uses vector embeddings to understand the intent behind user queries, not just the keywords.
- Context-Aware Results: Retrieves relevant culinary information based on ingredients, flavor profiles, and cultural context.
🛡️ Resilient Architecture
- Circuit Breakers: Protects external API integrations (like embedding services) from cascading failures.
- Queue-Based Processing: Ensures reliable data synchronization and heavy processing tasks using Bull and Redis.
📊 Comprehensive Monitoring
- Data Quality Service: Continuously monitors the consistency between the primary database and the vector store.
- Real-time Metrics: Tracks system health, sync status, and performance metrics.
RAG Implementation
The core of the system is its advanced RAG implementation, which ensures high availability and data consistency.
RAG Workflow
The system follows a streamlined Retrieval-Augmented Generation process to deliver accurate and context-aware responses.
flowchart TD
User[User Query]:::entity --> API[API Gateway]:::service
API --> Embed[Embedding Service]:::service
Embed -->|Generate Vector| GenAI[Google GenAI]:::external
GenAI -->|Vector| Embed
Embed --> Search[Vector Search]:::service
Search -->|Query Vector| Qdrant[Qdrant Vector Store]:::external
Qdrant -->|Relevant IDs| Search
Search --> Context[Context Retrieval]:::service
Context -->|Fetch Details| DB[PostgreSQL]:::external
DB -->|Food Data| Context
Context --> LLM[LLM Processing]:::service
LLM -->|Prompt + Context| GenAI
GenAI -->|Natural Response| LLM
LLM -->|Final Answer| User
classDef service fill:#007bff,stroke:#0056b3,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
classDef entity fill:#28a745,stroke:#1e7e34,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
classDef external fill:#fd7e14,stroke:#e8590c,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
Queue-Based Processing Architecture
To handle high loads and ensure data consistency, K-Food uses a dual-queue system for processing RAG operations.
graph LR
subgraph "Queue System"
A[rag-sync]:::external --> B[Primary Processing]:::service
C[rag-sync-retry]:::external --> D[Retry Processing]:::service
end
subgraph "Processors"
E[RagSyncProcessor]:::service --> B
F[RagRetryProcessor]:::service --> D
end
subgraph "Workers"
G[Worker 1]:::service --> E
H[Worker 2]:::service --> E
I[Worker 3]:::service --> F
end
classDef service fill:#007bff,stroke:#0056b3,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
classDef external fill:#fd7e14,stroke:#e8590c,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
System Architecture
The application is built on a modern stack ensuring scalability and performance.
- Frontend: Next.js 16 with React 19, utilizing React Query for state management and TailwindCSS for styling.
- Backend: NestJS 11 providing a robust server-side architecture.
- Database: PostgreSQL for relational data and Qdrant for vector embeddings.
- AI Integration: Google GenAI (Gemini) for generating embeddings and natural language responses.
- Infrastructure: Redis for caching and job queues, with cloud storage integration (AWS S3/GCP).